Preservation of Water Quality
Data on the quality of water has been accumulated through periodical observations. While this fixed-point observation is continued, an automatic water quality monitoring system named "Shiraberu," which can perform 24-hour observation, constantly monitors the quality of the Nagara river water. When localized temporary deterioration of water quality arises unexpectedly, gates are operated to make a flushing action possible to enhance water quality.
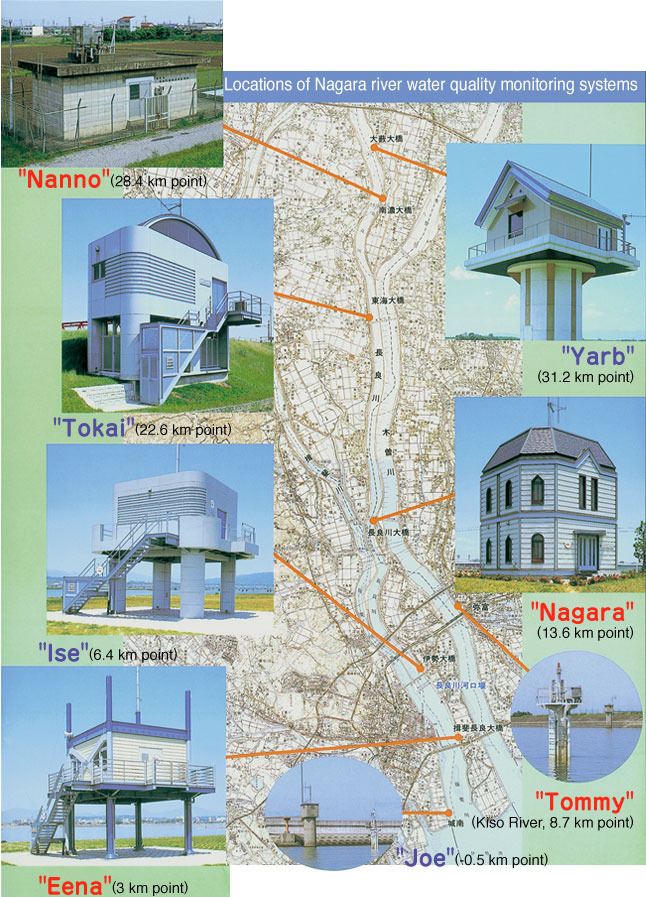
"SHIRABERU" (Automatic Water Quality Monitoring System)
This is a round-the-clock facility for the monitoring the quality of Nagara river water. Monitoring systems are installed at eight sites to observe necessary monitoring items constantly.
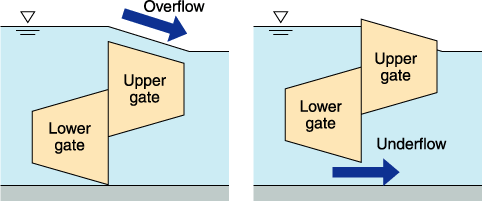
Water quality enhancement through gate operation(flushing action)
When DO (dissolved oxygen) decreases or chlorophyll a increases, the amount of inflow into the barrage is temporarily increased to enhance water quality.

Patrol at the water surface level
To restore clear streams, the Urgent Action Plan for the Improvement of Water Environment (Clear Stream Renaissance 21) was formulated in fiscal 1993 through 2000 in the tributaries that flow into the middle reaches of the Nagara River, namely the Sakai, Arata, Shin-arata, Ronda and Kuwabara Rivers. Under the plan, comprehensive and prioritized water quality enhancement measures have been taken jointly by the local municipal governments, river administrators and sewerage managers. In the Kuwabara River, environmental quality standards were not satisfied at designated points. The second-phase Urgent Action Plan for the Improvement of Water Environment (Clear Stream Renaissance II) was therefore developed and water quality enhancement measures have been taken since fiscal 2001.
Branch Stream Purification Program
Water purification facilities are installed to improve the quality of the water from the tributaries of the Nagara River. In purification facilities, river water is cleansed in two stages. The first mainly involves removing SS through the use of recycled polypropylene, while in the second stage, empty containers of lactic acid bacteria beverages are used to reduce BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) and other parameters.
Planned treatment capacity
- Sakai river water purification facilities 6.4 m3/s
- Kuwabara river water purification facilities 0.7 m3/s

Sakai river water purification facilities